Linux常用定制
Note
符号说明:
SDK$:指代源码路径。
console$:泛指主板的命令行控制台。
ADB$:Android Debug Bridge 命令行工具,泛指可运行 ADB 的环境。
开机自启程序
开机自启动脚本:
操作示例:
赋予脚本运行权限,将开机启动程序命令添加至kickpi.sh脚本中,实现开机自启。
串口自动登录修改
通过串口登录时,默认登陆root,参考此处操作修改为kickpi
vim /lib/systemd/system/serial-getty@.service
-ExecStart=-/sbin/agetty --autologin root --keep-baud 115200,38400,9600 %I $TERM
+ExecStart=-/sbin/agetty --autologin kickpi --keep-baud 115200,38400,9600 %I $TERM
修改桌面登录为root
图形化界面默认登录为kickpi,修改相关配置,重新启动后登录用户为root。
Ubuntu
修改默认登录用户
重启
Debian
修改默认登录用户
添加root登录权限
$ sudo vim /etc/pam.d/lightdm-autologin
--auth required pam_succeed_if.so user != root quiet_success
++#auth required pam_succeed_if.so user != root quiet_success
重启
Ubuntu修改用户名
1. 参考上文,修改全部默认登录用户为root。
2. 启动后修改hostname
3. 修改用户名
Tip
kickpi-new:新用户名
kickpi: 旧用户名
4. 设置新用户名目录
5. 清除图像化界面缓存
6. 重新配置silm图像化
语言配置
Tip
命令执行完成后,需重启才能生效。
Ubuntu2004
- 设置英文语言
$ locale-gen en_US.UTF-8
$ sed -i 's/^# *\(en_US.UTF-8\)/\1/' /etc/locale.gen
$ echo "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" >> /etc/default/locale
$ echo "export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8" >> /etc/profile.d/zh_CN.sh
$ echo "export LANG=en_US.UTF-8" >> /etc/profile.d/zh_CN.sh
$ echo "export LANGUAGE=en_US:en" >> /etc/profile.d/zh_CN.sh
- 设置中文语言
$ locale-gen zh_CN.UTF-8
$ sed -i 's/^# *\(zh_CN.UTF-8\)/\1/' /etc/locale.gen
$ echo "LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> /etc/default/locale
$ echo "export LC_ALL=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> /etc/profile.d/zh_CN.sh
$ echo "export LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> /etc/profile.d/zh_CN.sh
$ echo "export LANGUAGE=zh_CN:zh" >> /etc/profile.d/zh_CN.sh
时区配置
Tip
命令执行完成后,需重启才能生效。
- 设置时区亚洲/上海
- 设置时区美国/纽约
开机 LOGO
Note
1. rockchip 平台区分 Uboot、Kernel两个阶段显示LOGO,logo.bmp 为Uboot阶段,logo_kernel.bmp为Kernel阶段。
2. LOGO的分辨率必须小于显示屏的分辨率。
3. 替换的LOGO格式需和原本LOGO图片格式一致,例如bmp、bit 位等参数。
| 主控 | 型号 | LOGO路径 |
|---|---|---|
| A133 | K5/K5C | device/config/chips/a133/configs/c3/android/bootlogo.bmp |
| RK3562/RK3568/RK3588 | K1/K1B/K3/K8 | kerne/logo.bmp kernel/logo_kernel.bmp |
| RK3576 | K7/K7C | kernel-6.1/logo.bmp kernel-6.1/logo_kernel.bmp |
| T527 | K9 | device/config/chips/t527/boot-resource/boot-resource/bootlogo.bmp |
配置屏幕显示方向
- 查看当前屏幕信息
Tip
根据打印信息可知,当前系统为单屏幕显示,并且显示设备名称为 HDMI-1。
$ xrandr
Screen 0: minimum 320 x 200, current 1920 x 1080, maximum 16384 x 16384
HDMI-1 connected primary 1920x1080+0+0 (normal left inverted right x axis y axis) 0mm x 0mm
1920x1080 60.00*+ 60.00 50.00 59.94 30.00 24.00 29.97 23.98
1920x1080i 60.00 50.00 50.00 59.94
1280x1024 60.02
1440x900 59.90
1360x768 60.02
1280x720 60.00 50.00 50.00 59.94
1024x768 60.00
800x600 60.32
720x576 50.00 50.00
720x576i 50.00
720x480 60.00 60.00 59.94 59.94
720x480i 60.00 59.94
640x480 60.00 59.94 59.94
- 旋转屏幕显示方向
Note
normal:将显示设备正常的显示。
left:将显示设备逆时针旋转 90 度。
inverted:将显示设备顺时针旋转 90 度。
right:将显示设备旋转 180 度。
设置指定显示设备的旋转方向
操作示例:配置 HDMI-1 显示逆时针旋转 90 度。
- 触摸校准
1. 安装工具
2. 查看设备和ID,根据打印信息可知,当前触摸设备为"goodix-ts",id为10
3. 配置输入设备的校准矩阵
$ xinput set-prop $id --type=float "libinput Calibration Matrix" 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
操作示例:设置 goodix-ts 设备的校准矩阵
4. 配置输入设备坐标转换矩阵
// normal
$ xinput set-prop $id 'Coordinate Transformation Matrix' 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
// left
$ xinput set-prop $id 'Coordinate Transformation Matrix' 0 -1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
// right
$ xinput set-prop $id 'Coordinate Transformation Matrix' 0 1 0 -1 0 1 0 0 1
// inverted
$ xinput set-prop $id 'Coordinate Transformation Matrix' -1 0 1 0 -1 1 0 0 1
操作示例:根据旋转情况使用对应命令,设置 goodix-ts 设备的坐标转换矩阵为left
5. 校准触摸
操作示例:校准 goodix-ts 设备
- 开机自启动旋转服务参考
Ubuntu系统
root@ubuntu2004:~# vim /etc/systemd/system/xrandr-startup.service
[Unit]
Description=Start xrandr script on boot
After=graphical.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
Environment="DISPLAY=:0"
Environment="XAUTHORITY=/home/kickpi/.Xauthority"
ExecStart=/usr/bin/xrandr --output LVDS-1 --rotate left
User=kickpi
[Install]
WantedBy=graphical.target
Debian系统
vim /etc/systemd/system/xrandr-startup.service
[Unit]
Description=Start xrandr script on boot
After=graphical.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
TimeoutStartSec=10
Environment="DISPLAY=:0"
Environment="XAUTHORITY=/home/linaro/.Xauthority"
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/wait-for-x11.sh /usr/bin/xrandr --output DSI-1 --rotate left
User=linaro
[Install]
WantedBy=graphical.target
root@linaro-alip:/# cat /usr/local/bin/wait-for-x11.sh
#!/bin/bash
while ! xrandr --query > /dev/null 2>&1; do
sleep 1
echo "Waiting for X server to be ready..."
done
exec "$@"
永久修改触摸方向
xinput修改成功后,修改旋转触摸。
Tip
Option "TransformationMatrix" "0 -1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1" 为添加的内容
vim /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/40-libinput.conf
Section "InputClass"
Identifier "libinput touchscreen catchall"
MatchIsTouchscreen "on"
MatchDevicePath "/dev/input/event*"
Driver "libinput"
Option "TransformationMatrix" "0 -1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1"
EndSection
网络配置
静态IP地址配置
操作示例1:eth0网卡通过netplan的yaml配置静态IP地址为192.168.1.50
$ vim /etc/netplan/01-network-manager-all.yaml
network:
version: 2
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.199.160/24]
optional: true
routes:
- to: default
via: 192.168.199.1
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]
操作示例2:eth1网卡通过network/interfaces配置静态IP地址为192.168.77.196
$ sudo vim /etc/network/interfaces.d/eth1.cfg
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 192.168.77.196
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.77.1
dns-nameservers 8.8.4.4 8.8.8.8
重启服务
常用配置
- 显示所有网络接口信息
Tip
网络接口名称根据实际情况会有所不同。
$ ifconfig -a
enP3p49s0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
ether 82:76:b8:2f:96:6d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device interrupt 168 base 0xd000
enP4p65s0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
ether 6a:cb:0c:a5:15:e0 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device interrupt 179 base 0x1000
...
- 显示特定网络接口信息
Tip
要显示特定网络接口(如eth0)的信息,可输入ifconfig eth0。
- 设置 IP 地址
操作示例:要为eth0接口设置 IP 地址为192.168.1.101,子网掩码为255.255.255.0,
- 启用网络接口
- 禁用网络接口
操作示例:禁用eth0接口
- 设置 MAC 地址
Tip
不同操作系统间可能存在一些差异,部分系统可能不允许通过ifconfig直接设置或需额外步骤进行设置。
命令行配置WIFI热点(AP)模式
- 查看是否支持AP模式
Tip
AP/VLAN表示硬件支持。
$ iw list | grep AP
Device supports AP-side u-APSD.
* AP
* AP/VLAN
HE Iftypes: AP
HE Iftypes: AP
* wake up on EAP identity request
* AP/VLAN
* #{ managed } <= 1, #{ AP, P2P-client, P2P-GO } <= 1, #{ P2P-device } <= 1,
Driver supports full state transitions for AP/GO clients
Driver/device bandwidth changes during BSS lifetime (AP/GO mode)
* AP: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* AP/VLAN: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* AP: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* AP/VLAN: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
虚拟接口创建热点模式
1. 安装依赖包
2. 创建虚拟网卡
Note
< wirelessname > 是真实无线网卡名,可通过ifconfig查看,< virtualwlanname > 是虚拟的无线网卡名。
操作示例:
3. 为虚拟网卡添加物理地址
Tip
< virtualwlanname >是虚拟的无线网卡名,可随意填写,产生冲突更换命名即可。
操作示例:
4. 查看创建情况
Warning
重启系统后,创建的虚拟网卡会失效。
$ sudo iw dev wlo2 info
Interface wlo2
ifindex 5
wdev 0x5
addr 22:33:44:55:66:00
type managed
wiphy 0
txpower 0.00 dBm
multicast TXQ:
qsz-byt qsz-pkt flows drops marks overlmt hashcol tx-bytestx-packets
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5. 下载安装工具 create_ap
6. 使用create_ap创建热点
Note
< wirelessname > :无线网卡名称
< virtualwlanname > :虚拟网卡名称
< SSID > < password >:热点Wifi名称和密码。
操作示例:
如果创建的热点卡死,开启热点时报如下错误:
#RTNETLINK answers: Device or resource busy
#ERROR: Maybe your WiFi adapter does not fully support virtual interfaces.
# Try again with --no-virt.
停止之前创建的热点,重新启动开启热点。
物理接口创建热点模式
1. 安装依赖和create_ap
$ sudo apt-get install util-linux hostapd dnsmasq iptables iproute2 haveged make
$ git clone https://github.com/oblique/create_ap
$ cd */create_ap
$ sudo make install
2. 修改防火墙
$ sudo update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
$ sudo update-alternatives --set ip6tables /usr/sbin/ip6tables-legacy
$ iptables --version
3. 创建热点MyAccessPoint,密码:12345678,共享eth0网络
4. 使用 create_ap 后恢复 WiFi 节点
NFS配置
- 环境配置
- 服务器端
1. 配置共享的文件
$ mkdir /home/kickpi/nfs_share
$ chmod 777 /home/kickpi/nfs_share
$ vi /etc/exports
+ /home/kickpi/nfs_share *(rw,sync,no_subtree_check,insecure)
2. 启动服务
3. 查看当前服务器共享文件,证明共享成果
- 客户端
1. 查看服务器共享文件
2. 挂载文件夹
3. 挂载成功
镜像源设置
1. 查看软件版本,根据版本查找镜像源替换
$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS
Release: 20.04
Codename: focal
2. 修改软件源并更新源缓存
Tip
使用arm的镜像源。
Chrome 硬件加速测试
测试平台:RK3568 Debian11 Chrome
测试方法
1. 拷贝1080P及4K分辨率视频至开发板,通过Chrome浏览器本地解码。
2. 查看GPU占用:
3. 打开帧解码日志并打印:
export mpi_debug=1
export mpp_debug=1
export h264d_debug=1
export mpp_syslog_perror=1
echo 0x100 > /sys/module/rk_vcodec/parameters/mpp_dev_debug
测试结果
1080P_30帧/秒:GPU占用在42%-48%左右;每帧解码时间测试结果日志片段:
[ 639.172225] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 4195 us hw 4095 us
[ 639.180185] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 12116 us hw 7960 us
[ 639.190246] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 19541 us hw 10027 us
[ 639.199403] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 22900 us hw 9153 us
[ 639.203403] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 20805 us hw 4053 us
[ 639.213146] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 21496 us hw 9638 us
[ 639.222129] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 21700 us hw 9056 us
[ 639.228897] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 24810 us hw 6819 us
[ 639.403439] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 6511 us hw 6482 us
[ 639.411955] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 11883 us hw 8450 us
[ 639.420139] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 17932 us hw 8009 us
[ 639.429258] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 24691 us hw 9296 us
[ 639.503067] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 5224 us hw 5164 us
[ 639.509281] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 8586 us hw 6174 us
[ 639.518009] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 14440 us hw 8704 us
[ 639.529122] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2268:56 time: 22595 us hw 11125 us
4K_30帧/秒:GPU占用在60%-68%左右;每帧解码时间测试结果日志片段:
[ 938.649847] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 93967 us hw 27794 us
[ 938.683932] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 93243 us hw 34114 us
[ 938.717400] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 93712 us hw 33463 us
[ 938.751306] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 100528 us hw 33952 us
[ 938.780302] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 95406 us hw 28932 us
[ 938.813718] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 94942 us hw 33414 us
[ 938.838935] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 86479 us hw 25243 us
[ 938.872539] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 91289 us hw 33486 us
[ 938.906450] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 91721 us hw 33970 us
[ 938.942726] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 102481 us hw 36284 us
[ 938.960331] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 86302 us hw 17609 us
[ 938.994526] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 86494 us hw 34091 us
[ 939.025353] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 80775 us hw 30825 us
[ 939.058137] rk_vcodec: fdf80200.rkvdec:0 session 2799:80 time: 96464 us hw 32684 us
SSH 配置
默认不支持root连接,root连接需要配置
$ vim /etc/ssh/ssh_config
+ PermitRootLogin yes
$ vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
+ PermitRootLogin yes
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
Tip
确保开发板IP正常,能正常连通开发板IP。
$ cat /etc/ssh/ssh_config | grep PermitRootLogin
PermitRootLogin yes
$ cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep PermitRootLogin
PermitRootLogin yes
USB 摄像头
- 检查摄像头设备节点
- ffmpeg 打开摄像头
操作示例:
UBUNTU从官网安装软件包
操作示例:
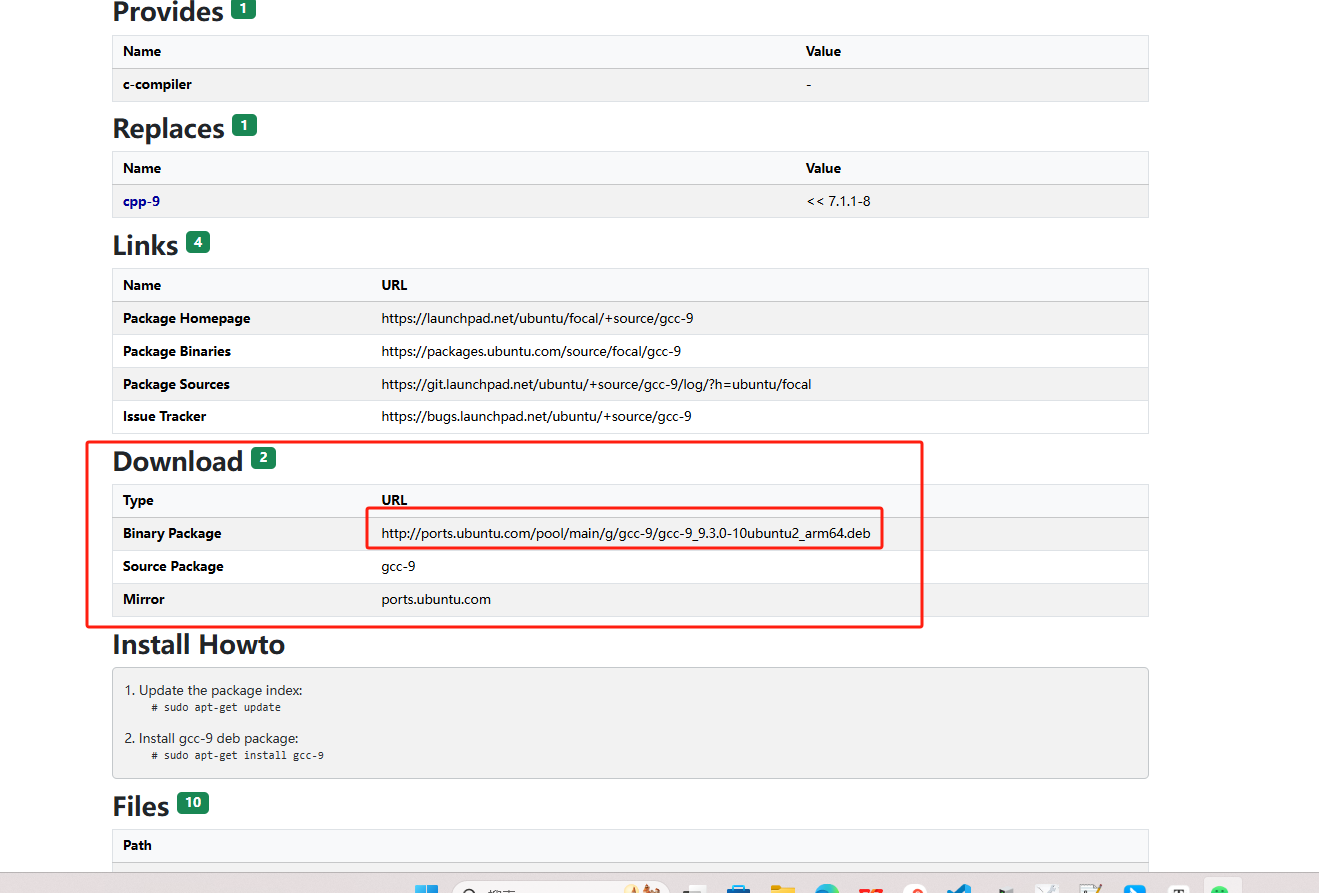
安装gcc
从官网中获取依赖包名
备份rootfs系统
Tip
通过这种方式替换后的rootfs可能存在mount挂载UUID问题,通过blkid查看正确的UUID,修改/etc/fstab。
接好U盘在板子上,大小至少16GB以上,打包出来的镜像会比较大
1. 插入U盘(≥ 16GB),将脚本拷贝至开发板Linux系统上运行
Note
生成包名格式:例如 rootfs.img。 /mnt/usb :U盘挂载目录。
2. 确保打包出来的文件格式正确
Tip
FAT32单文件不可超出4G,如果系统太大,请格式化U盘为ext4、exfatg格式。
$ file Ubuntu_24.04.2_LTS_ext4_202503062020.img
Ubuntu_24.04.2_LTS_ext4_202503062020.img: Linux rev 1.0 ext4 filesystem data, UUID=71584b93-ad99-452e-a8e2-6b9ed76eff7d, volume name "rootfs" (extents) (64bit) (large files) (huge files)
3. 重新打包,将rootfs.img替换进完整镜像,参考固件解包和打包;也可单独烧录rootfs.img,烧录完成后,根文件系统占用的存储空间与镜像文件(img)大小一致,执行命令还原大小。
eMMC分区
Warning
重新分区均需要重新烧录,如需保留系统,不进行格式化,请先备份rootfs。
可通过两种方式完成修改:
- 完整镜像修改
参考固件解包和打包,修改parameter.txt文件后重新打包。
- SDK内修改
对应路径下文件修改完成后,重新编译。
RK356x:
RK3588:
修改内容:
重新分区主要修改分区文件parameter.txt
操作示例:将剩余所有空间放至根目录下
mtdparts=:0x00002000@0x00004000(uboot),0x00002000@0x00006000(misc),0x00020000@0x00008000(boot),0x00040000@0x00028000(recovery),0x00010000@0x00068000(backup),-@0x00078000(rootfs:grow)
Note
文件分区规则:
分区大小:0x01c00000*512Byte/1024/1024/1014 ≈ 14G
分区起始地址:前一个分区起始地址+前一个分区大小
最后一个分区格式为:-@0x0xxxxx(xxx:grow) -表示剩余所有空间自适应。
Linux系统需要额外增加一步修改,注释oem userdate的自动挂载。
Ubuntu桌面版进入root用户
Note
最新桌面版系统默认登录用户为:kickpi
桌面版系统的 Terminal 使用某些命令时可能需要root权限,在命令添加sudo 或进入root用户。
操作步骤:
1. 设置root密码
Tip
输入当前用户密码例如:kickpi 。
New Password:输入要设置的root密码 (密码不显示)。
Retype new password:再次确认。
password updated successfully:表示成功。
2. 切换到root用户
进入Linux命令行界面
Ubuntu系统
关闭Ubuntu图形化桌面会进入Linux命令行界面,本章节介绍如何开关Ubuntu图形化桌面。
Note
GUI 桌面被冻结使用键盘进入命令行界面。
输入快捷键 CTRL + ALT + F3 进入命令行界面。
输入快捷键 ALT + F2 返回 GUI 桌面。
- 暂时关闭桌面
- 临时启动桌面
- 永久禁用桌面
- 永久启动桌面
Debian系统
- 禁止桌面环境
修改默认的运行模式
查看当前系统运行模式
重启
- 启用桌面环境
修改默认的运行模式
重启
Samba 安装
1. 安装samba
2. 给予共享的文件权限
3. 添加samba用户
4. 配置samba
在smb.conf末尾处添加以下内容:
Tip
[kickpi] 为共享看到的文件夹名称
5. 重启服务
RKNN 部署
系统支持部署 rknn-toolkit2,rknn_model_zoo,点击跳转至 Rockhip 官方文档。
常见问题
@@ -321,9 +321,9 @@ can_transmit_to_channel() {
if [[ $USE_IWCONFIG -eq 0 ]]; then
if [[ $FREQ_BAND == 2.4 ]]; then
- CHANNEL_INFO=$(get_adapter_info ${IFACE} | grep " 24[0-9][0-9] MHz \[${CHANNEL_NUM}\]")
+ CHANNEL_INFO=$(get_adapter_info ${IFACE} | grep " 24[0-9][0-9]\(\.0\+\)\? MHz \[${CHANNEL_NUM}\]")
else
- CHANNEL_INFO=$(get_adapter_info ${IFACE} | grep " \(49[0-9][0-9]\|5[0-9]\{3\}\) MHz \[${CHANNEL_NUM}\]")
+ CHANNEL_INFO=$(get_adapter_info ${IFACE} | grep " \(49[0-9][0-9]\|5[0-9]\{3\}\)\(\.0\+\)\? MHz \[${CHANNEL_NUM}\]")
fi
[[ -z "${CHANNEL_INFO}" ]] && return 1
[[ "${CHANNEL_INFO}" == *no\ IR* ]] && return 1
@@ -339,7 +339,9 @@ can_transmit_to_channel() {
# taken from iw/util.c
ieee80211_frequency_to_channel() {
- local FREQ=$1
+ local FREQ_MAYBE_FRACTIONAL=$1
+ local FREQ=${FREQ_MAYBE_FRACTIONAL%.*}
if [[ $FREQ -eq 2484 ]]; then
echo 14
elif [[ $FREQ -lt 2484 ]]; then
@@ -356,7 +358,7 @@ ieee80211_frequency_to_channel() {
}
is_5ghz_frequency() {
- [[ $1 =~ ^(49[0-9]{2})|(5[0-9]{3})$ ]]
+ [[ $1 =~ ^(49[0-9]{2})|(5[0-9]{3})(\.0+)?$ ]]
}